Using an advanced translation environment such as memoQ offers many benefits to anyone involved in the translation of eLearning and online training content. memoQ is both powerful and flexible and can fit into whatever translation process is most useful for your particular situation.
Please note:
* Step 1 is written primarily from the perspective of the eLearning content creator.
* The remaining steps are written primarily from the perspective of a translator working on a project with one target language.
* Keep in mind that the memoQ server is ideal for large, complex localization projects that can include collaborative teams, many languages, frequent source updates, etc.
Here’s a quick look at the basic steps in localizing eLearning content and how you can use memoQ in the process.
Process for translating eLearning content from source language A to target language B
1. Prepare the source content/eLearning components for translation
Available: eLearning content in the source language (A) that requires translation into one or more target languages
Source content is typically created by different people and can be in many different file formats. The files can be from any of many different components within the learning system. For example:
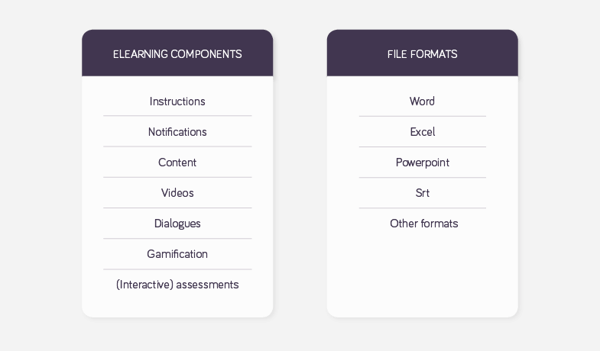
A review round after the creation of the eLearning components is advised.The better the quality and consistency of the source material, the better the translation will be, whether using translation memories (TM) and human translators or machine translation (MT) and human post-editors .
A controlled, consistent creation of the source material following clearly defined rules can lead to a better translation.
Some of the editorial issues that should be addressed prior to translation include:
- Are there any length/space/time restrictions?
- Is there proprietary or industry-specific terminology to be followed?
- What is the formality/style (how do you prefer to address course participants, what is the tone, etc.)?
Your requirements for these and any other editorial concerns should be communicated to the translator and others involved in the project.
If your eLearning organization already has memoQ, you can use it to pre-translate the final edited source content with existing translations before sending them out for human and/or machine translation.
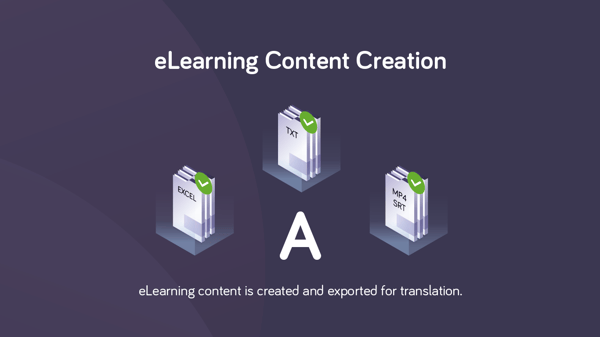
The source content identified for translation is exported from the digital learning environment or eLearning platform. This can be the full course or selected components.
Note: If the source language (A) is not English, it is sometimes first translated into EN, which then serves as the source.
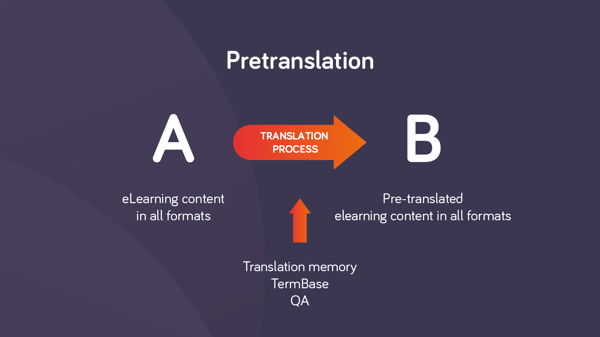
2. Translation
Available: The translator receives eLearning content in the source language (A) and translates it into target language B.
A single project with a single TM can contain the entire project, regardless of the various file formats (memoQ can handle them all). The translator uses memoQ to translate all the content, updating the TM as segments are completed in order to maximize leverage and ensure consistency for repetitive and similar segments.
In the case of multiple translators working in the same language at the same time, an online project on a memoQ server is the ideal environment. It enables real-time sharing of TMs, term bases, and maximizes leverage.
Translation into multiple languages can take place simultaneously, whether by individual translators working independently or online.
Remember: Any changes to your translation must be fed back into your translation memory at any times. It happens automatically if you work within memoq (which we suggest as the prefered way). If you need to do a later editing round, you should make sure not to lose these changes and manually enter them into the TM.
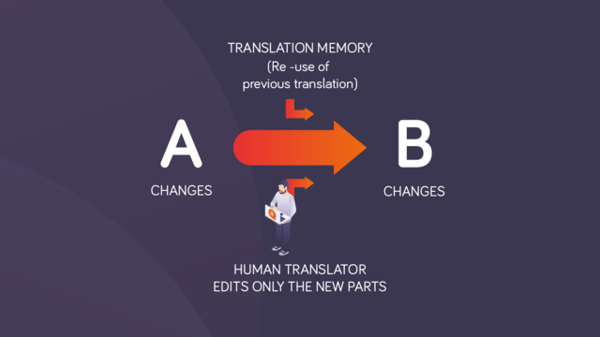
3. Source text revisions
Available: eLearning content with changes in the source language (A or EN) and the translation memory with the existing translation in the target language (B).
There can be frequent changes to the source text, causing the need for corresponding changes in the translated text. Using a TM and updating it whenever a change is made ensures that the most current translated content will always be available.
The changed content in the source language is pre-translated in memoQ with the TM, automatically reusing previous translations. Existing translations in the TM, along with term bases, and other resources in memoQ, help produce a quick and consistent translation of the changes.
During rounds of source text revision, the previously translated text is reused, making this step faster and less prone to error than translating from scratch or manually identifying and making updates. Human translators are still crucial to this work, but technology minimizes the repetitive tasks. Pre-translation also works as well for small and last-minute updates as it does for larger, planned revisions.
Note: memoQ updates the TM with revisions so as to have the latest version always available. This happens automatically if a memoQ server is used.
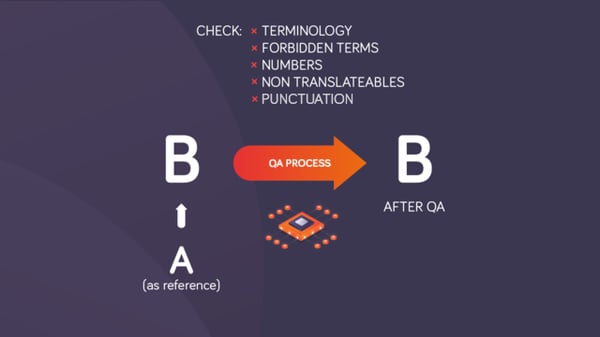
4. Translation Quality Assurance
Available: eLearning content in the source language (A or EN) and a translation in the target language (B).
The translated content in the target language is typically reviewed by another qualified human translator. Human nature being what it is, some human reviewers/editors might want to change not only the target translation but also the source content, whether due to errors or preferences. If the eLearning doesn’t have a policy for handling these changes, be prepared with your own plan, including whether they should be suggested to the eLearning organization for incorporation in the source text.
memoQ’s automated technical QA should also be included in the process. Translation technology adds value with a variety of automated quality checks while also making the process faster, more efficient, and more consistent. (The translator can run certain QA checks while translating, too.)
If the eLearning organization also has memoQ, it’s a good idea for them to run memoQ’s QA checks one last time before the translation is reimported into the eLearning system.
5. Delivery
The final translation (translated, edited, QA checks run, and any last-minute source text revisions to your translation made) is delivered to the eLearning organization where it will be imported into the eLearning platform.
Ask your client to inform you of any post-delivery changes they make so you can incorporate them into your TM and term base. This will help insure consistency in your next eLearning project for this client.
Summary: The memoQ team works tirelessly to make it the preferred tool for your eLearning translations. Use memoQ to automate and optimize your eLearning localization process and manage translation projects in a cost-efficient manner. memoQ handles virtually all file formats in one user-friendly platform, saving you both time and hassle. T.
We provide translation technology to translators, project managers, and trainers, helping them work efficiently and productively in the dynamic, exciting eLearning industry.
By the way: The memoQ training team offers online training on many different topics. Check out the new online training sessions for Project Managers and Translators. We hope they will improve your productivity and make memoQ even more valuable for you.

Angela Starkmann
Linguist, editor, PM and communication specialist with broad experience in software and documentation localization, translation of marketing material.




