Translating your eLearning Content
Since the COVID-19 confinement began, people have been interacting online more than ever, and not just for work or social contact. eLearning and Blended Learning (a learning experience with both online and traditional face-to-face instruction) are everywhere now—for formal education, continuing professional education, and lifelong learning. English isn’t the only language in demand, either. There is an ever-increasing demand for more online training courses in more languages and more subjects.
Translation and localization is crucial in creating content that is easy to use and appealing to learners who need to interact online with their instructors and peers.
From a translator’s perspective, working with content for multilingual eLearning courses is not very different from working with other sorts of online content. However, it is surprising to see that standard translation technologies and best practices are not yet commonly used in the eLearning industry. This is a missed opportunity for reaping the benefits of translation memory, terminology management, and automated QA, not to mention the possibility of potential for savings with machine translation integrations. memoQ, when used for eLearning projects, can be a valuable quality assurance tool and productivity driver, and makes projects readily accessible for anybody who translates the training materials. Whether translators are professionals, local trainers, or subject matter experts—memoQ is user-friendly, intuitive, and will do wonders for the translation workflow of any online learning content.
eLearning is usually managed in a Learning Management System (LMS) and often bundled with other components into a full-blown multimedia environment. Translation of the content should be done by qualified translators, whether internally or through a Language Service Provider (LSP). Whatever the process you choose, memoQ makes it easy to manage translation of the various file formats you encounter (.csv, .xml, .srt, and many others) consistently and professionally into your learners’ languages.
Translation for eLearning is not just about translating words from one language to another, though. It is also about localization—a comprehensive process that includes not only translating but also adjusting cultural and non-textual components ;and resolving the linguistic issues that arise when adapting a product or service for another country or locale. eLearning is being adopted on a global scale. Translation technology is the gold standard for getting content ready for an international audience.
Workflow
Most companies develop a custom workflow for the localization of eLearning modules that fits their operational needs. There can be many workflow variations, but these are the essential components:
*Text extraction. Any text to be translated first needs to be extracted from the LMS software. memoQ works with almost any file format with ease.
*Translation. Translation and localization are done by skilled linguists. Translators will benefit from the many advantages of their translation environment as they do in other translation projects. Translation memories, term bases, concordances, QA checks, and other features make it possible to work consistently and efficiently even when your project contains many different files and file formats.
*Translation review: memoQ also facilitates the translation review process. You can assign roles to your translators and reviewers. memoQ keeps a complete version control for everything that has been changed, added, or deleted throughout the process.
*Multimedia production: Translation of any audio or audiovisual translation can also be done for each new language version. This could be subtitled videos or translation of audio text that is prepared prior to a voiceover recording by native speakers. memoQ is a great tool for handling translation of audiovisual material
*Reimport: All text and multimedia components are imported back into the module.
*Quality assurance: Automated quality checks offer a technology-based check of format and linguistic consistency. After that, language experts do an extensive usability check to make sure standards are met and that all components work together seamlessly.
Components
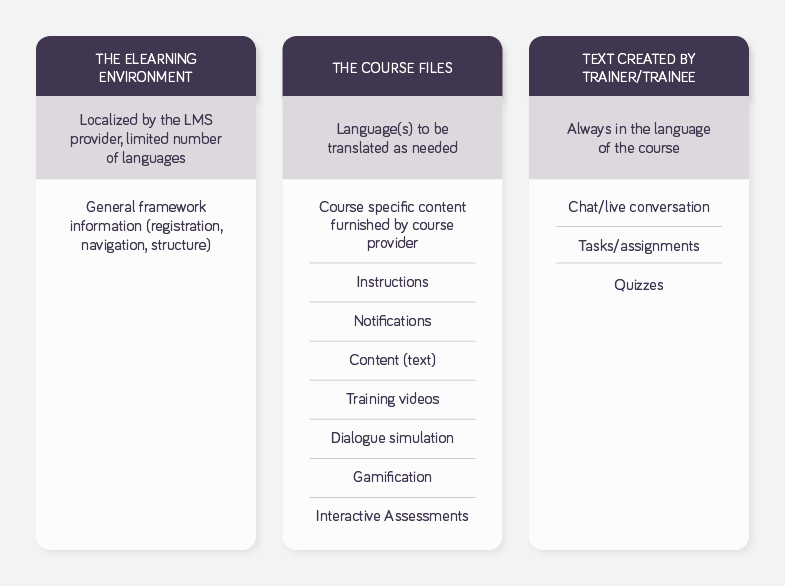
In order to understand the localization of eLearning material, it is important to understand the different elements of text to be presented to the student. Content may be created by different people and can be in diverse formats.
First, there’s the framework of the digital learning environment (or eLearning platform). The students see general framework information (such as information on how to register, how to navigate, or what to do in certain situations). This is created by the authors of the eLearning platform. Usually, these text elements are already localized in a limited number of languages that can typically not be changed. (Make sure the languages you want to work with are offered when selecting an eLearning platform.)
Second, there’s the actual course material. This is specific information that can be in almost any format. For example, there might be custom-made instructions written especially for the course or digital content in many different file formats. Course content is created by one or several authors (often the actual trainers of a course) for use by the course participants, and can be exported from the eLearning system for translation. Ideally, the content exported from the LMS for translation will then be imported into a translation tool like memoQ. Project management, translation, and editing in the memoQ translation environment enables you to process almost any file formats (such as Word, Excel, or SRT, to name a few) features like translation memories, terminology management, machine translation, and batch operations, just like with any other types of translation jobs.
The third type of content is text that is generated directly in the course of conversations between trainers and trainees. It can be chat, another form of live conversation, or written text from student assignments. This content usually will not be translated but is spoken or written in the language of the actual course, often in real time.
Learning is most effective when applied directly to the daily life of learners. It should connect to people emotionally with language and cultural aspects that make them feel at home. A strategic approach to localization is needed to make sure that as many common cultural aspects as possible are included to connect trainers and trainees, no matter where they are. When adapting a module for a specific locale, all examples, scenarios, and the like should be offered in a manner that suits the background of a particular audience. This is a critical aspect of the translation and localization process.
Look for translators who have not only the pertinent subject matter expertise, language skills, and experience with translation tools, but who also understand the specifics of the targeted local market. Appropriately localized training will engage your learners even before the training begins. And memoQ will be onboard with you every step of the way.
By the way: The memoQ training team offers online training on many different topics. Check out the new online training sessions for Project Managers and Translators. We hope they will improve your productivity and make memoQ even more valuable for you.
Want to Start Localizing your eLearning Content?

memoQ
memoQ is among the world's leading translation management systems. The favorite productivity tool for translation professionals around the globe.





